We investigate supplier credit qualification thoroughly, to control the quality since the very beginning. MT Electronics has its own QC team, can monitor and control the quality during the whole process including in-coming, storage, and delivery and etc.
Contracted with the global authorities third-party testing power, by using the most advanced testing machine, each of the high precision parts is tested strictly to ensure that its stability and compatibility can meet its own specification.
Anti-static, moisture-proof and damage-prevention methods & packages will be adopted strictly during the stock and delivery procedure. We undertake the responsibility to return or replace the parts which exactly have quality issues.
- Visual Inspection
- X-ray Inspection
- Marking Permanency Test
- De-capsulation Test
- Pin Assignment Test
- PB Free / RoHS Test
- Electrical Test
- Functional Test
External Visual Inspection (EVI):
The first, and most essential, step for any component evaluation is a thorough inspection process. Our procedure and acceptance standards have been developed in order to detect and report evidence of remarking, resurfacing, and refurbishing.
Marking permanency and resistance to solvents, resurfacing, dimension verification, marking code matching, high-power magnification inspection of the body and terminal condition are standard methods within our inspection process. All inspections and observations are reviewed by Quality Engineers to evaluate whether we are seeing a new counterfeiting technique or a manufacturing anomaly.

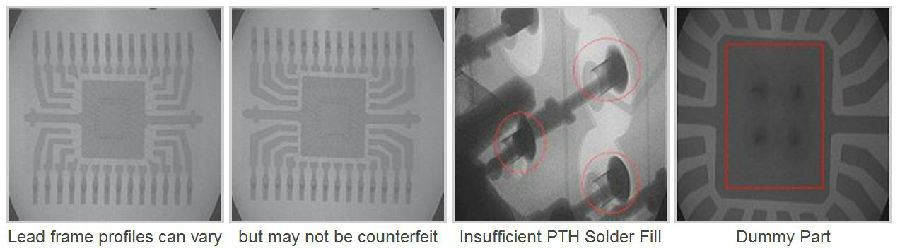
Radiography (X-ray):
Inspection and analysis of a component to examine hardware integrity and variations between devices within a population. Not all variations, however, mean a counterfeit device. Understanding the manufacturing process and how manufacturer supply chains and engineering controls operate, we can identify when variations are manufacturing-based rather than indicators of counterfeiting.
X-ray system is real-time and can rotate the object on all three axes for outstanding imaging capability and analysis of individual components and assembled boards.
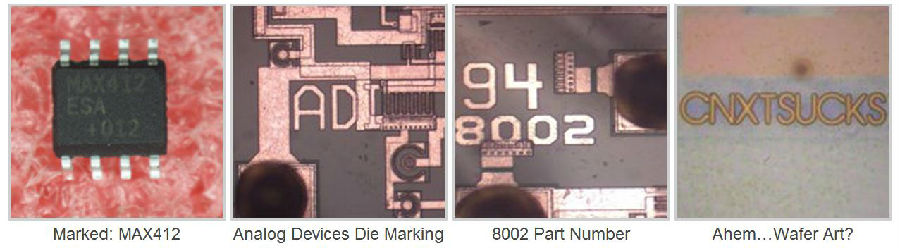
Decapsulation:
A destructive test that removes the insulation material of the component to reveal the die. The die is then analyzed for markings and architecture to determine the traceability and authenticity of the device. The magnification power of up to 1,000x is necessary to identify die markings and surface anomalies.
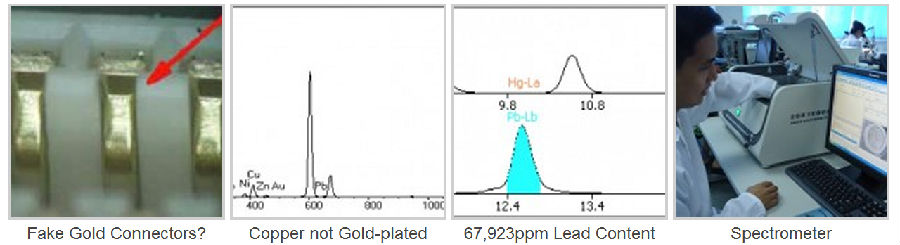
X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Material Analysis:
The spectrometer is used for measuring the controlled elements in lead-free and RoHS compliant devices and determining the composition of plating materials. We also use this equipment for helping to detect reconditioned and resurfaced parts by measuring the plating thickness and variations in the composition of the surface material.
Solderability Testing:
This is not a counterfeit detection method as oxidation occurs naturally; however, it is a significant issue for functionality and is particularly prevalent in hot, humid climates such as Southeast Asia and the southern states in North America. The joint standard J-STD-002 defines the test methods and accept/reject criteria for thru-hole, surface mount, and BGA devices. Devices that are delivered in inappropriate packaging, acceptable packaging but are over one year old or display contamination on the pins are recommended for solderability testing.



























































































